D100
California Mastitis Test (CMT)
Introduction:
The California Mastitis
Test (CMT) is a rapid, accurate, animal-side test to help determine somatic cell
counts (SCC). The term somatic cell is used to identify any cell in the body.
With the CMT test, the somatic cells that are being measured are mainly
neutrophils. Neutrophils are white blood cells that help the body fight
infection and are present in increased numbers in the udder when the animal has
mastitis. The CMT test was developed to sample individual udder halves to
determine the presence of subclinical mastitis. The test can also be conducted
on bucket and bulk tank milk samples to help determine somatic cell counts (SCC)
of the entire herd.
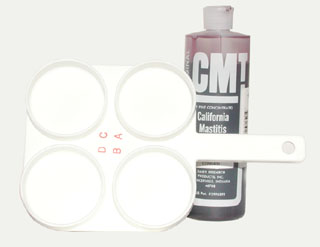 |
|
|
| California
Mastitis Test. |
|
How to Perform the Test: A small sample of milk (approximately ½
teaspoon) from each teat is collected into separate compartments of a plastic
paddle that has shallow cups marked A, B, C and D. An equal amount of CMT
reagent is added to the milk. The paddle is rotated to mix the contents. In
approximately 10 seconds, the score should be read, while continuing to rotate
the paddle. Because the reaction disappears within 20 seconds, the test must be
read quickly.
 |
|
|
| Clean
each teat with alcohol. Squirt a small amount of milk from each teat
into the appropriate section of the paddle. 1/2 teaspoon of milk is
sufficient. |
|
 |
|
|
| Mix
an equal ratio of reagent to milk. The
paddle is rotated to mix the contents. |
|
 |
|
|
| In
approximately 10 seconds, read the score while continuing to rotate
the paddle. This goat has a negative CMT score. |
|
How to Read the Results: The CMT reagent
reacts with the neutrophils, and the mixture thickens or gels in proportion to
the amount of cells that are present. High levels of neutrophils indicate
infection. To become accurate and consistent, practice this test on animals with
a known SCC.
| CMT Score |
Average Somatic Count (Cells per milliliter) |
Description of reaction |
| N (negative) |
0-480,000 |
No thickening, homogeneous. |
| T (trace) |
up to 640,000 |
Slight thickening. Reaction disappears in 10 seconds. |
| 1 |
660,000 |
Distinct thickening, no gel formation. |
| 2 |
2,400,000 |
Thickens immediately, begins to gel, levels in the bottom of cup. |
| 3 |
>10,000,000 |
Gel is formed, surface elevates, with a central peak above the mass |
Treatment: Refer to the mastitis
information found on page F500.




