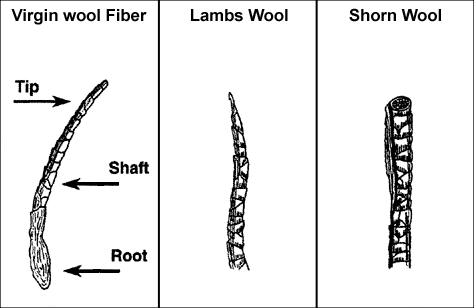
Introduction:
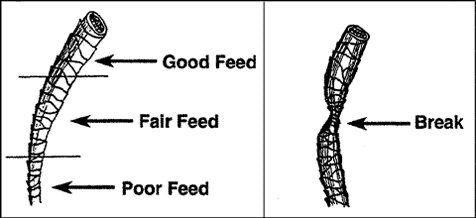
The true wool fiber is basically modified hair that is not shed like the hair of most farm animals. Nutrition can cause differences in fiber diameters and fiber strength. A sheep on a high plane of nutrition grows a coarser fiber than one on a poor ration. A break or tender spot in the fiber can be caused by an extreme drop in nutrition or from stress caused by an infection, illness, or pregnancy. Shorter daylight hours also result in a smaller fiber diameter, regardless of nutritional levels. The tip of a fiber on a lambís fleece is pointed, while the tip from a mature fleece is flat because of previous shearing. The wool fiber, for descriptive purposes, is divided into three (3) sections: the root, shaft, and tip.
| Breed | No. of Follicles/mm2 (Primary and secondary) |
Number of Primary Follicles/mm2 |
S:PRatio |
| Fine Merino | 71.7 | 3.56 | 19.1 |
| Medium Merino | 64.4 | 2.93 | 21.0 |
| Strong Merino | 57.1 | 3.27 | 16.5 |
| Corriedale | 28.7 | 2.43 | 10.8 |
| Southdown | 27.8 | 3.9 | 6.3 |
| Dorset | 18.5 | 2.9 | 5.4 |
| Suffolk | 20.4 | 3.5 | 4.8 |
| Romney | 22.0 | 3.4 | 5.5 |
| Border Leicester | 15.8 | 2.9 | 4.4 |
| Lincoln | 14.6 | 2.3 | 5.4 |
| Cheviot | 14.6 | 2.7 | 4.5 |
| Wiltshire | 11.4 | 2.6 | 3.3 |
| Characteristic | True Wool | Kemp | Heterotype (hair) |
| Structure | Epidermis Cortex |
Epidermis Cortex Medulla |
Epidermis Cortex Medulla |
| Length | Long | Short to 1 Ĺ inch | Long |
| Diameter | Same for entire length | Tapers at root and tip | Same for entire length |
| Transparency | Semi-transparent | Opaque | Semi-opaque |
| Crimp | Yes | No, has wave | Long, open crimp |
| Surface | Prominent scales | Scales | Few scales set close to fiber |
| Elasticity | Good | Poor | Fair |
| Root | None | Present | None |