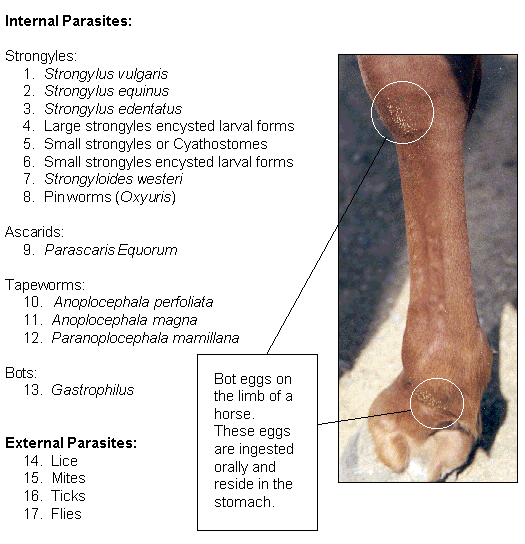

Clinical Signs: Signs of infection are most common in young, very old or diseased animals. Most parasite infections cause weight loss, unthriftiness and poor weight gains. Some parasites can cause diarrhea, decreased appetite, and colic. If the parasites are migrating through the lungs, there may be coughing and nasal discharge. If the infection is extremely severe, death may occur.
Disease Transmission: Each one of the internal parasites is spread by orally ingesting the parasite in its infective stage. This most commonly occurs during grazing. The external parasites are spread by direct contact or having infested animals in close association with other animals.
Diagnosis:
Treatment/Prevention: Differences in treatment are based on the common parasites encountered and the geographical location in which a particular horse resides. It is recommended that a local veterinarian be consulted for specifics on timing and frequency of treatments. The following are a few of the available products:
For Internal Parasites:
|
Product Trade Name |
Active Ingredient |
**Effective Against |
|
Ivermectin |
#1-3, 5, 7-9, 13 |
|
|
Moxidectin |
#1-9, 13 |
|
|
Pyrantel |
#1-3, 5, 7-12 |
|
|
Dyrex |
Piperazine |
# *1, 5, *8, 9 |
|
Oxybendazole |
#1-3, 5, 7-9 |
|
|
Panacur |
Fenbendazole |
#1-3, 5, 7-9 |
*
This product is effective against S. vulgaris and Oxyuris only 40-60% of the time.Additional Management Ideas:
External Parasites: There are many different sprays and pour-ons that are effective against most external parasites. It is important to remember to read the product label to ensure that each specific product can be given to horses. Pay close attention to dosage and administration instructions.